目录
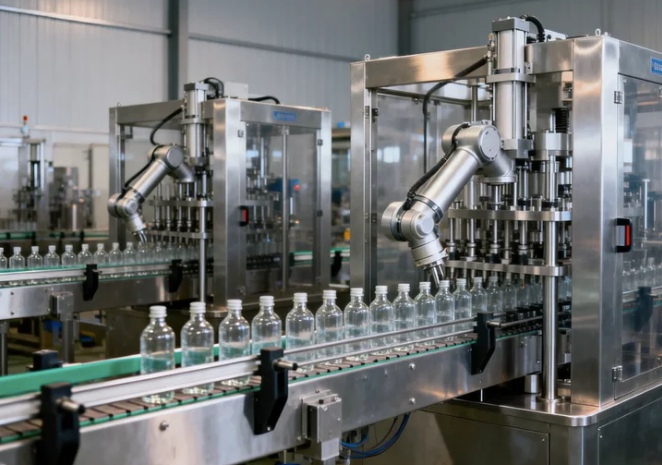
A filling capping machine is a crucial component of modern production lines, ensuring that products are accurately filled and securely sealed. Despite their advanced design, filling capping machines can experience operational problems that reduce efficiency and affect product quality. Understanding the most common issues and implementing proper solutions is essential to maintain smooth operations, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of the equipment

Inconsistent Filling Volumes
(1)Causes
- Improper calibration of the filling system can lead to variations in product volume between bottles.
- Clogged or worn-out filling nozzles may disrupt flow and affect accuracy.
- Changes in product viscosity, especially for liquids that may thicken or separate, can impact the filling consistency.
(2)Solutions
- Calibrate the filling system regularly, checking accuracy for different container sizes. Some liquid filling capping machines can achieve ±1% filling precision, which should be verified periodically.
- Clean and inspect nozzles to prevent blockages. Using quick-disassembly nozzles can make maintenance easier.
- Adjust machine parameters to accommodate changes in product properties. For example, increase pump speed slightly for thicker liquids to maintain the target fill volume.
(3)Practical Tip
- Operators should track filling deviations using in-line scales or sensors to quickly identify irregularities. Filling speeds for standard liquid machines typically range from 40 to 100 bottles per minute, and any consistent deviation should trigger immediate inspection.
Misaligned or Missing Caps
(1)Causes
- Poor synchronization between the capping mechanism and the conveyor system can result in skipped or improperly positioned caps.
- Worn cap delivery belts or faulty sorters may fail to feed caps correctly.
- Variations in bottle height or shape can prevent proper alignment during capping.
(2)Solutions
- Regularly inspect and adjust conveyor speed to maintain synchronization with capping heads.
- Replace worn or damaged components in the cap feeding system.
- Standardize bottle sizes where possible, and use adjustable guides to accommodate slight variations.
(3)Extended Advice
- Semi-automatic filling capping machines are particularly sensitive to misalignment because manual loading introduces inconsistencies. Fully automatic systems often include sensors that detect missing caps and stop production, preventing defective products from reaching packaging.
Leaking or Dripping Nozzles
(1)Causes
- Damaged seals or gaskets on nozzles can cause leaks during filling.
- Misaligned nozzles may result in uneven flow, producing drips.
- Residual pressure in the pump or pipeline can force excess product after filling stops.
(2)Solutions
- Replace seals and gaskets on a scheduled maintenance cycle, typically every 500 operating hours.
- Verify nozzle alignment before production, ensuring they match the container opening accurately.
- Implement a short depressurization cycle at the end of each fill to prevent dripping.
(3)Additional Tip
- Machines handling viscous products like sauces or creams require slower fill speeds and larger nozzle openings to reduce dripping, which can improve product presentation and minimize waste.
Bottle Jams or Tipping
(1)Causes
- Incorrect conveyor speed or misaligned rails can cause bottles to tip or jam.
- Non-uniform bottles may not sit properly on conveyor guides, leading to stoppages.
- Gripper belts or pushers that are worn or improperly tensioned can fail to move bottles smoothly.
(2)Solutions
- Adjust conveyor speed and guides to match the bottle type. Production lines can vary from small benchtop setups to high-speed systems capable of 9,000 bottles per hour, and speed adjustments are critical for each type.
- Inspect and replace gripper belts regularly.
- Ensure bottles meet uniform size and shape standards for consistent flow.
(3)Operational Advice
- High-speed filling capping machines may include anti-jam sensors that detect bottle misalignment. These systems can pause the line and alert operators, preventing damage to the machine and product.
Inconsistent Torque on Caps
(1)Causes
- Incorrect torque settings on capping heads may under-tighten or over-tighten caps.
- Worn capping heads lose accuracy over time.
- Variations in cap dimensions or material stiffness can affect applied torque.
(2)Solutions
- Calibrate torque settings according to manufacturer recommendations and product requirements. Typical torque ranges vary depending on container size and cap type.
- Replace worn capping heads to maintain consistent sealing quality.
- Adjust machine parameters when switching between different cap types.
(3)Best Practices
- Implementing torque monitoring sensors can improve consistency and reduce customer complaints due to leaking or difficult-to-open caps. Regularly document torque settings and check results during production runs.
Conclusion
Efficient operation of a filling capping machine requires attention to detail, proactive maintenance, and timely troubleshooting. By addressing issues such as inconsistent filling volumes, misaligned caps, nozzle leaks, bottle jams, and torque variations, manufacturers can maintain high production efficiency and product quality.
Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and careful calibration are essential to extend machine life and ensure smooth, uninterrupted operation. Properly managed, filling capping machines can deliver reliable performance across liquid, paste, powder, and granule products, supporting long-term production goals.
0