目录
In today’s digital world, websites are not just platforms for sharing information—they are critical channels for interaction between businesses and users. Yet, studies show that nearly 98% of websites have some accessibility issues, making it difficult for users with special needs, such as visual impairments, hearing difficulties, mobility limitations, or color blindness, to navigate them. Independent website design and customization offers a tailored approach, enhancing website accessibility and creating a more inclusive, user-friendly experience for all users.
What Is Accessible Design?
According to the World Health Organization, over 2.2 billion people worldwide have some form of visual impairment, and approximately 466 million people have disabling hearing loss. Beyond legal compliance and ethical responsibility, accessible design improves usability, engagement, and satisfaction. With independent website design and customization, businesses and individuals can tailor layouts, colors, fonts, and interactive elements to meet specific accessibility requirements.
For example, adjusting text size, contrast, and spacing can improve readability for low-vision users, while customizing navigation structures can help users with mobility or cognitive challenges complete tasks 30–50% faster compared to poorly structured websites.
WCAG Standards and Customizable Design

The WCAG offers a comprehensive framework for developing websites that are fully accessible to all users. It focuses on four key principles: perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust design, ensuring that websites meet diverse user needs and adapt to various accessibility requirements.
- Structure pages with semantic HTML, ensuring that screen readers can easily navigate and interpret different sections of the page. Proper use of tags like <header>, <footer>, and <main>improves accessibility for users with visual impairments.
- Organize interactive elements for keyboard navigation, so users who cannot use a mouse can still navigate and interact with the site using only the keyboard. Make sure users can navigate through all links, buttons, and forms in a clear, sequential order using the Tab key.
- Adjust color schemes and improve contrast to accommodate users with color vision deficiencies, making content clearer and more distinguishable for all. About 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women are colorblind, so offering high-contrast or colorblind-friendly options significantly improves accessibility.
- Easily update and refine features as accessibility standards evolve. This allows for continuous improvement in compliance with WCAG, making websites more adaptable to user needs and legal requirements. Many websites can improve accessibility by up to 90% by following these guidelines.
By offering these customizable options, websites become more inclusive, ensuring that users with various disabilities can access and interact with the content as seamlessly as possible.
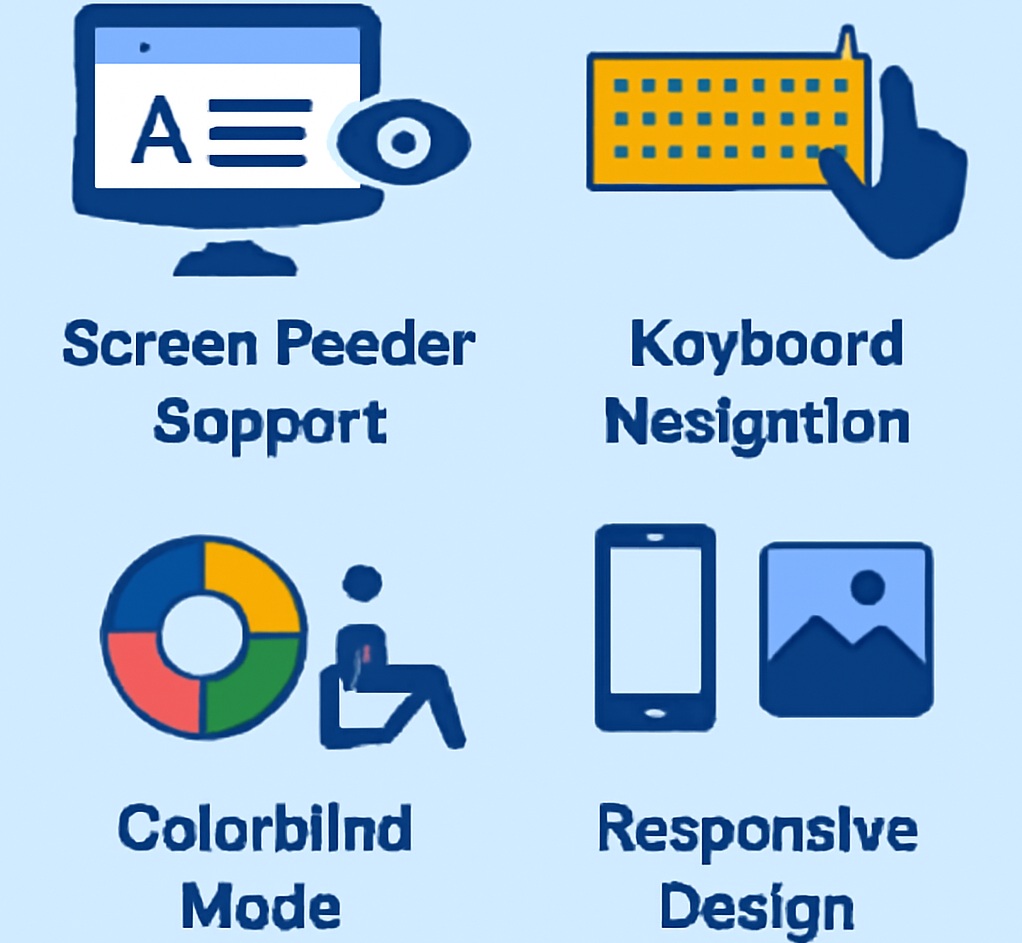
Key Accessible Design Features
Screen Reader Support
- Use semantic HTML for headings, lists, and sections
- Provide descriptive alt text for all images
- Use clear and concise labels for buttons, links, and form fields to improve usability
Statistic: Screen reader users report up to 40% faster navigation when semantic HTML is properly used.
Keyboard Navigation
- Ensure that all interactive elements can be easily accessed and navigated using the Tab and Enter keys, providing smooth keyboard navigation for users with mobility impairments.
- Maintain logical focus order for smooth browsing
- Implement keyboard shortcuts for efficiency in frequently used actions
Colorblind Mode and High-Contrast Design
- Avoid relying solely on color to convey meaning
- Offer colorblind-friendly palettes and high-contrast modes
- Supplement color with icons, patterns, or text labels for clarity
Responsive and Mobile-Friendly Design
- Adjust layouts automatically for different screen sizes
- Support touch interactions for mobile users
- Include captions and audio descriptions for videos to assist users with hearing or vision impairments
Benefits of Independent Website Design and Customization
- Adapt accessibility features for specific user groups: Customization allows designers to make adjustments like larger fonts, high-contrast color schemes, or simplified navigation for users with visual or cognitive impairments.
- Quickly optimize elements to meet WCAG standards: By tailoring the design, developers can easily implement features like semantic HTML or improved contrast to meet WCAG guidelines, reducing accessibility errors by up to 80%.
- Provide a scalable, sustainable solution: Customized designs allow for continuous updates as user needs evolve. This flexibility makes it easier for websites to grow and remain accessible over time, ensuring long-term compliance with accessibility regulations.
This approach ensures websites are both visually appealing and accessible, improving user engagement and expanding the potential audience.
Conclusion
By leveraging independent website design and customization, web designers can actively optimize websites for people with visual, hearing, mobility, or cognitive challenges. Combining WCAG compliance with features such as screen reader support, keyboard navigation, and colorblind-friendly modes ensures that websites are truly accessible for everyone.
Ultimately, independent website design and customization enables creators to build inclusive websites that improve user satisfaction, increase reach, and promote social responsibility. Proper implementation can boost task completion by 20–50% and significantly expand audience reach.
0